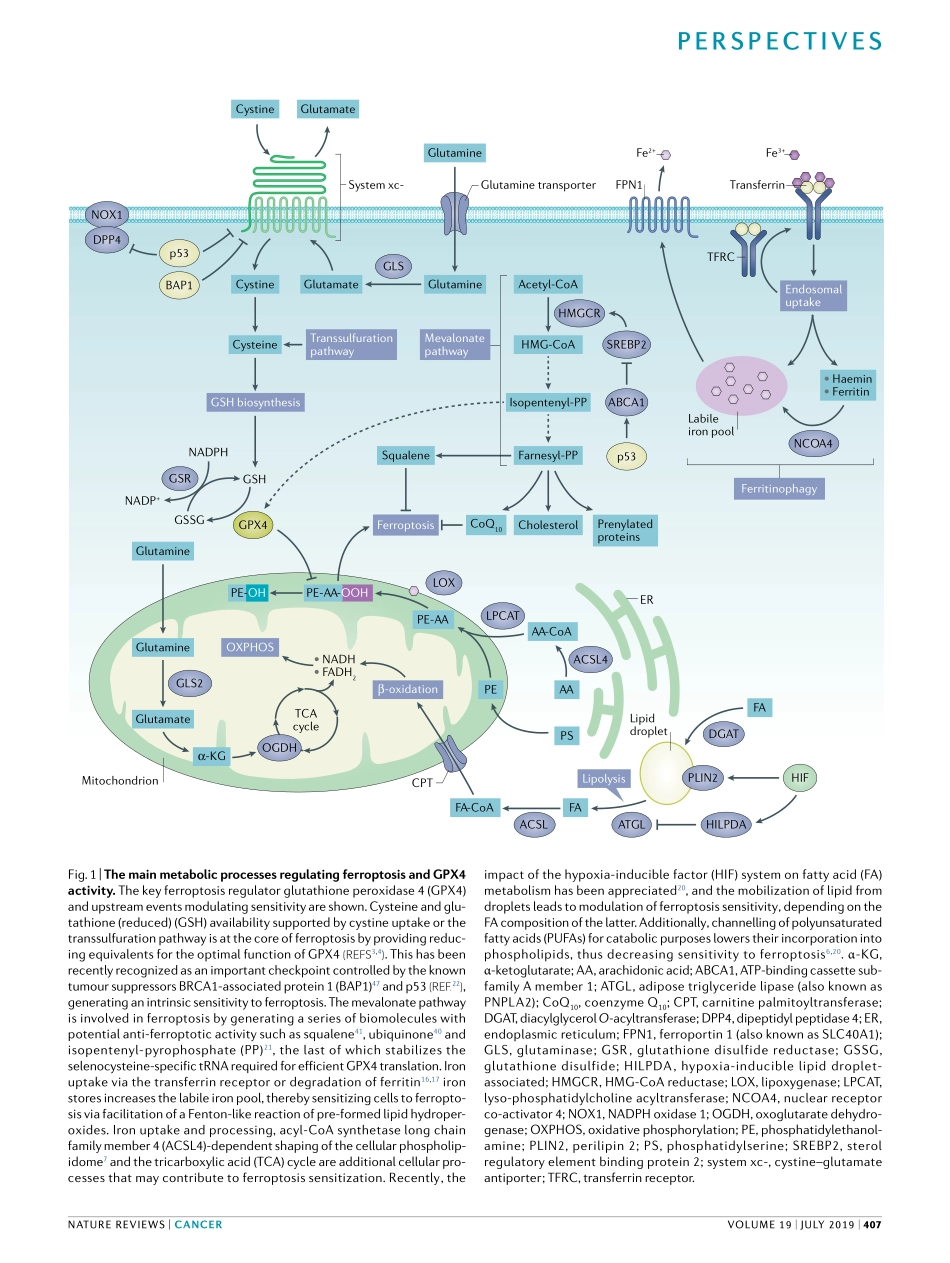
Ferroptosisisaformofnecroticcelldeathmarkedbytheoxidativemodificationofphospholipidmembranesviaaniron-dependentmechanism1.Aninitialcharacterizationofthispathwaydemonstratedthatcysteinedepletion,whichleadstotheexhaustionoftheintracellularpoolofglutathione(reduced)(GSH)specificallytriggersthisformofcelldeath2.TherequirementforGSHtoprotectfromferroptosiswaslaterrelatedtotheoptimalactivityoftheenzymeglutathioneperoxidase4(GPX4),aselenoproteinrequiredfortheefficientreductionofperoxidizedphospholipids3–5andtosuppresstheactivationofarachidonicacid(AA)-metabolizingenzymes6,whichmaycontributetotheprocessofphospholipidperoxidation.Sincethen,acomplexinterplaybetweenlipid,ironandcysteinemetabolismhasemergedasanimportantregulatorofthiscelldeathpathway.havealsoputforwardtheimportanceoftransferrintraffickingandferritindegradationthroughtheprocessofferritinophagy,aspecificformofautophagyrequiredforthedegradationofferritin,ascriticaldeterminantsofferroptosissensitivityviaanincreaseintheso-calledlabileironpool15–18.Despitethegeneralimportanceofthispathwaytosustainingcellsurvivalinnon-cancerouscellsandtissues19,ithasbeendemonstratedthatseveraloncogenicpathwaysrendercancercellsextremelysusceptibletothisformofcelldeaththroughthemodulationofkeyregulatoryferroptosischeckpoints20–24.Therecognitionthatoncogenicsignallinggeneratesaninherentferroptosissensitivityputsforwardacuriousdilemma:howcanthedownregulationofmechanismsthatsuppressferroptosis,associatedwithanincreaseinthesteady-statelevelsoflipidperoxidation,provideagrowthorsurvivaladvantagetocancercells?Spurredbythisapparentparadox,inthisOpinionarticle,wepresentadiscussionoftherecentadvancesintheunderstandingofferroptoticprocessesandofferaperspectiveonhowthemodulationofkeyelementsregulatingferroptosissensitivitycouldultimatelyimpingeontheinteractionsofcancercellswiththeimmunecompartment.WeprovideaGPX4-centricviewofhowthemodulationofkeymetabolicdeterminantsthatultimatelyimpactontheactivityofthiscriticalpro-survivalproteincontrolsrel...