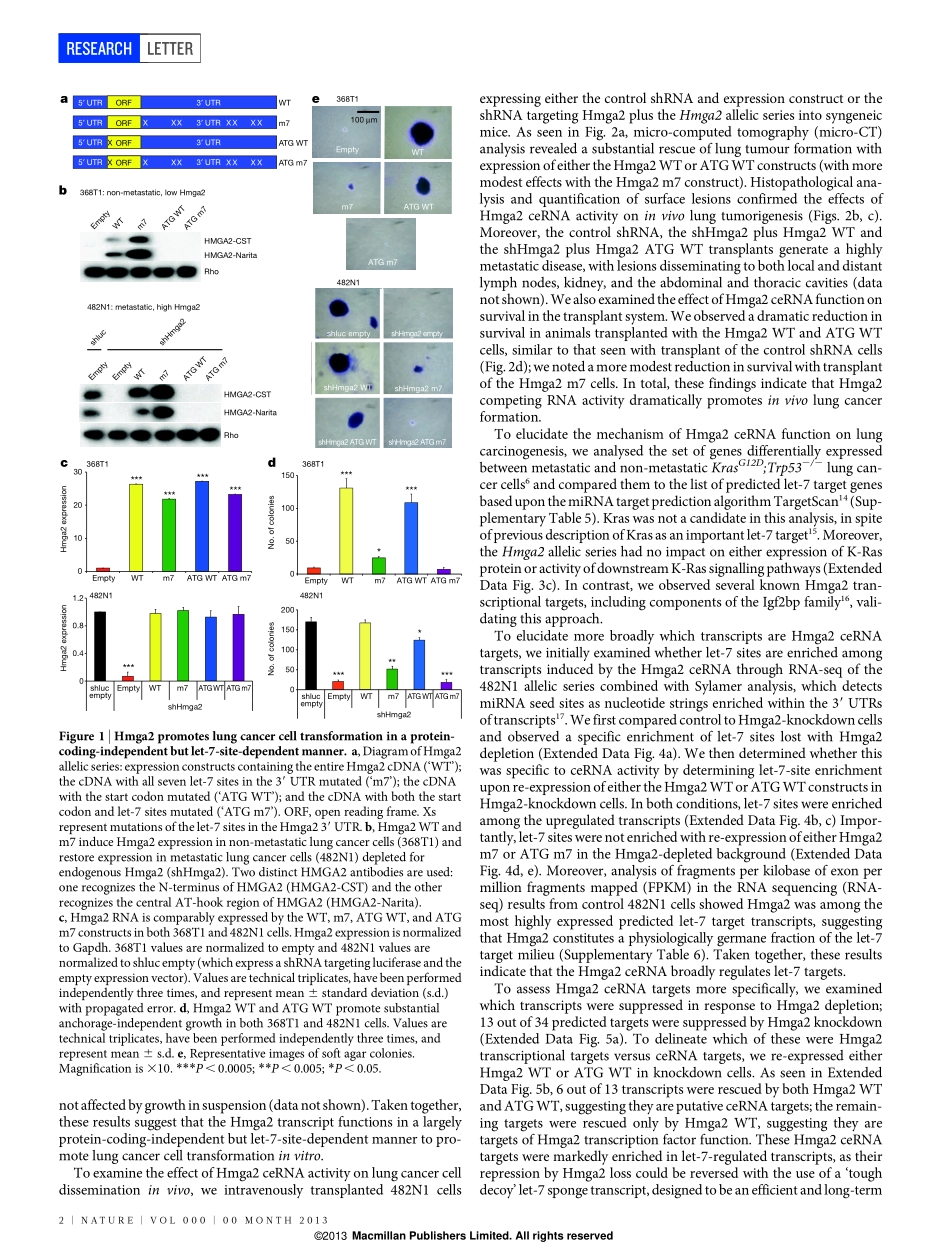
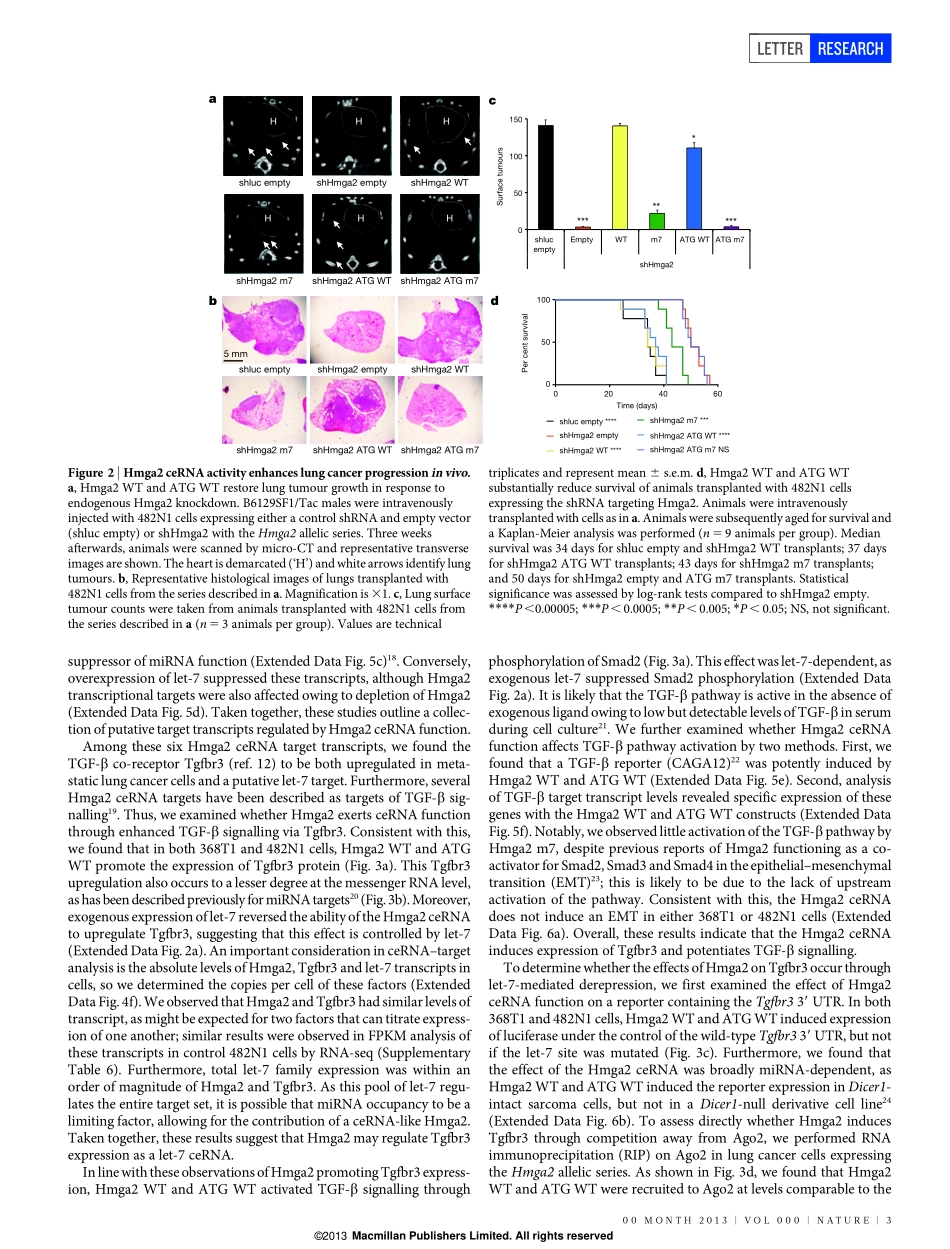
LETTERdoi:10.1038/nature12785HMGA2functionsasacompetingendogenousRNAtopromotelungcancerprogressionMadhuS.Kumar1,ElenaArmenteros-Monterroso1,PhilipEast2,ProbirChakravorty2,NikMatthews3,MonteM.Winslow4&JulianDownward1,5Non-small-celllungcancer(NSCLC)isthemostprevalenthistolo-gicalcancersubtypeworldwide1.Asthemajorityofpatientspre-sentwithinvasive,metastaticdisease2,itisvitaltounderstandthebasisforlungcancerprogression.Hmga2ishighlyexpressedinmetastaticlungadenocarcinoma,inwhichitcontributestocancerprogressionandmetastasis3–6.HereweshowthatHmga2promoteslungcancerprogressioninmouseandhumancellsbyoperatingasacompetingendogenousRNA(ceRNA)7–11forthelet-7microRNA(miRNA)family.Hmga2canpromotethetransformationoflungcancercellsindependentofprotein-codingfunctionbutdependentuponthepresenceoflet-7sites;thisoccurswithoutchangesinthelevelsoflet-7isoforms,suggestingthatHmga2affectslet-7activitybyalteringmiRNAtargeting.Theseeffectsarealsoobservedinvivo,whereHmga2ceRNAactivitydriveslungcancergrowth,invasionanddissemination.IntegratedanalysisofmiRNAtargetpredictionalgorithmsandmetastaticlungcancergeneexpressiondatarevealstheTGF-bco-receptorTgfbr3(ref.12)asaputativetargetofHmga2ceRNAfunction.Tgfbr3expressionisregulatedbytheHmga2ceRNAthroughdifferentialrecruitmenttoArgonaute2(Ago2),andTGF-bsignallingdrivenbyTgfbr3isimportantforHmga2topromotelungcancerprogression.Finally,analysisofNSCLC-patientgene-expressiondatarevealsthatHMGA2andTGFBR3arecoordinatelyregulatedinNSCLC-patientmaterial,avitalcorollarytoceRNAfunction.Takentogether,theseresultssuggestthatHmga2pro-moteslungcarcinogenesisbothasaprotein-codinggeneandasanon-codingRNA;suchdual-functionregulationofgene-expressionnetworksreflectsanovelmeansbywhichoncogenespromotedis-easeprogression.TheceRNAhypothesispositsthatspecificRNAscanfunctionassinksforpoolsofactivemiRNAs,functionallyliberatingothertran-scriptstargetedbythatsetofmiRNAs10.Downregulationofthetran-scriptionfactorNkx2.1promoteslungadenocarcinomaprogressionpartiallythroughder...