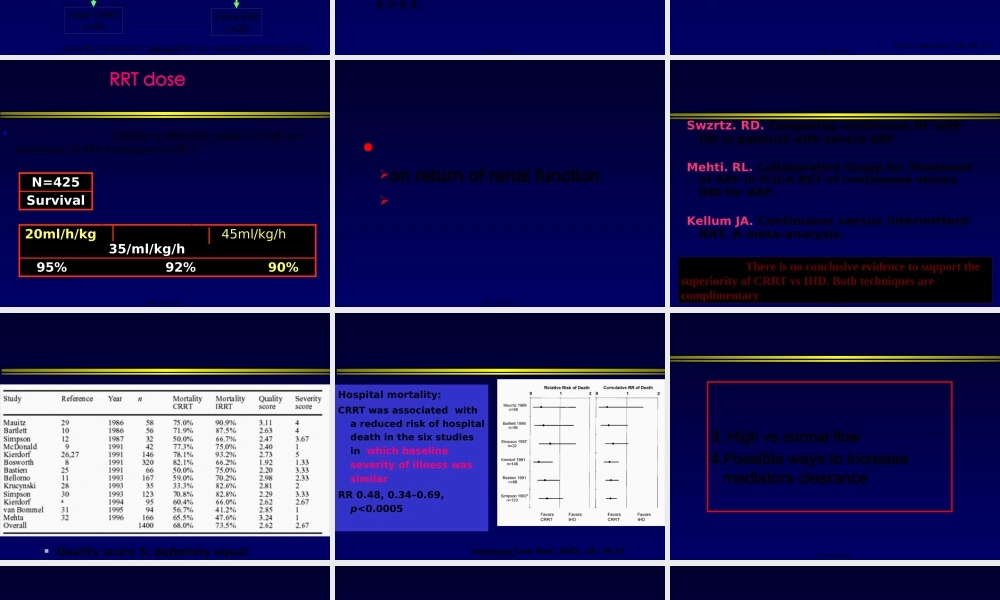
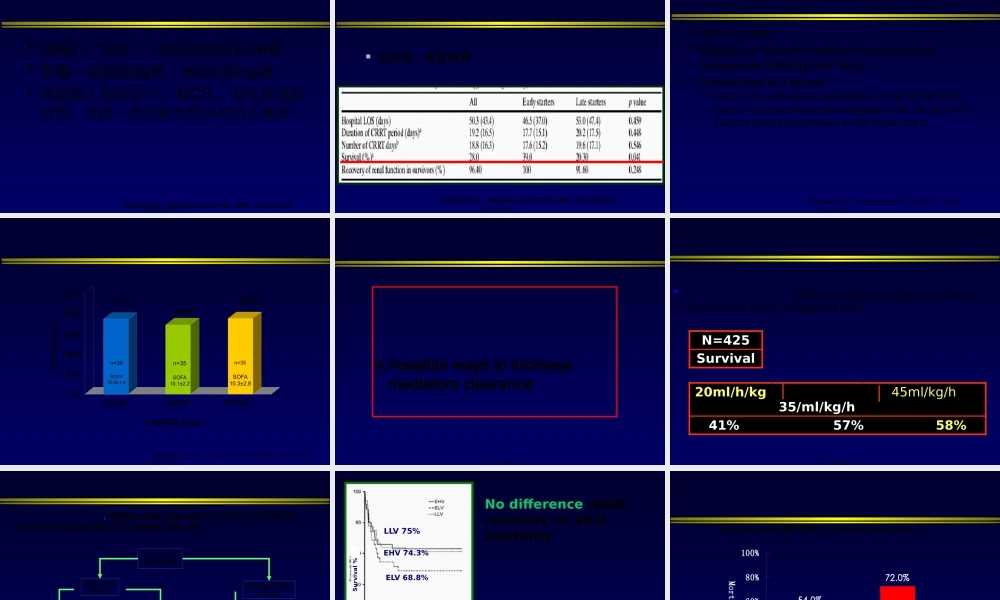
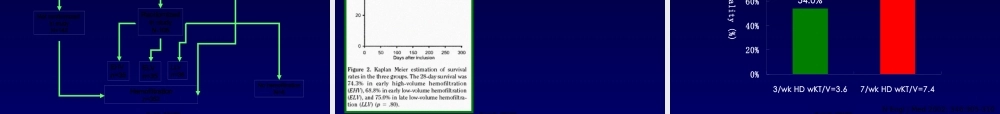
邱海波东南大学附属中大医院ICU东南大学急诊与危重医学研究所第一页,共四十四页。2.EarlyvslateCRRT3.Highvsnormalflow4.Possiblewaystoincreasemediatorsclearance第二页,共四十四页。0%20%40%60%80%100%AsiaAustraliaEuropeNorthAmericaSouthAmericaContinuousIntermittentOtherBellomo,etal.2001UnderstandingRenalReplacementTherapyandAcuteRenalFailureintheICU(TheB.E.S.Tkidneystudy)第三页,共四十四页。•Retrospectivecohortstudy•PatswithARFandrequireddialysisbetweenApril1,1996,andMarch31,1999•2ICUinCanada.•N=261CRRTIHDPAPACHEII2725.10.10BaselineSCr1361800.002MAPBeforeRRT74.787.2<0.001HospMortality71.9%42.2%<0.01Renalrecoveryinhosp80.0%62.5%0.06DurationofRRT14.7d14.5d0.91Costperweek(Can$)3486-51171341Survivor(Costpery)No-RRTRRT$11,192$73,273CritCareMed2003;31:449–455第四页,共四十四页。ICURRTn=116RRTforoverdosen=7Pre-existingCRFn=16ICURRTforARF/MOFn=66InitialCRRTn=66InitialIHDn=28JackaMJ,IvancinovaX,GibneyRTN.CanJAnaesth2005;52:327-332第五页,共四十四页。•Munnsetal观察危重急性肾衰竭患者IHDCRRT•CCr下降25%7%•尿量下降50%10%•钠排泄分数下降46%12%肾功能下降的原因:IHD平均动脉压下降,导致肾脏低灌注,加重肾脏缺血性损伤,延迟急性肾衰竭肾功能的恢复第六页,共四十四页。•160patswithARF:Dailyvsevery-other-dayIHD•Mean–Daily:1.2±0.5L–Every-other-day:3.5±0.3L(P<0.001).•occurredin–Daily:5±2%–Every-other-day:25±5%(P<0.001)•––NEnglJMed2002;346:305-310第七页,共四十四页。RRTdoseP=NS•EffectsofdifferentdosesinCVVHonoutcomesofARF:AprospectiveRCT20ml/h/kg35/ml/kg/h45ml/kg/h95%92%90%N=425Survival第八页,共四十四页。onreturnofrenalfunction第九页,共四十四页。Swzrtz.RD.ComparingcontinuousHFwithHDinpatientswithsevereARFMehti.RL.CollaborativeGroupforTreatmentofARFinICU:ARCTofcontinuousversusIHDforARF.KellumJA.ContinuousversusintermittentRRT.Ameta-analysis.ThereisnoconclusiveevidencetosupportthesuperiorityofCRRTvsIHD.Bothtechniquesarecomplimentary第十页,共四十四页。Qualityscore5:definitelyequal第十一页,共四十四页。Hospitalmortality:CRRTwasassociatedwithareducedriskofhospitaldeathint...