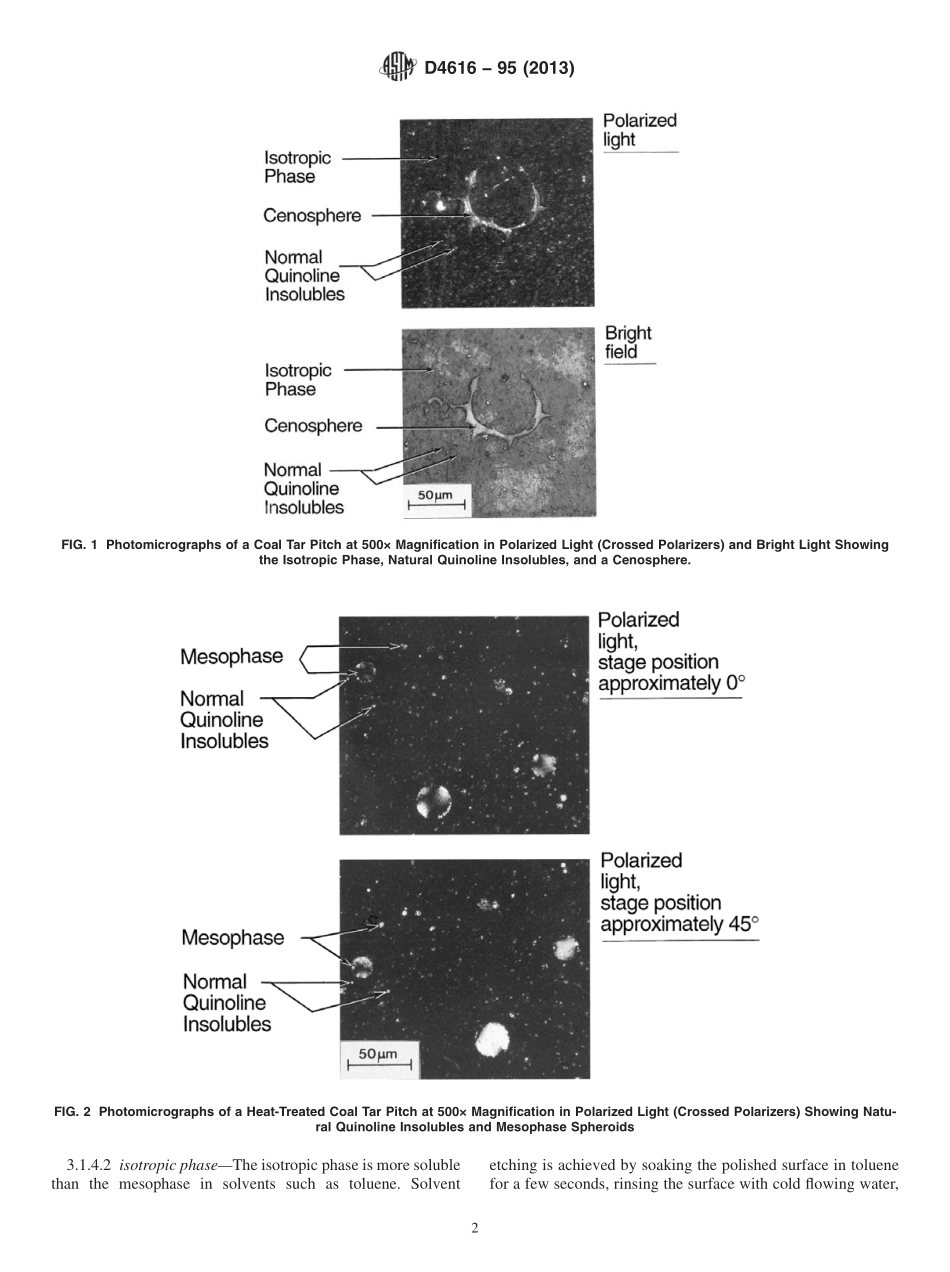
Designation:D4616−95(Reapproved2013)StandardTestMethodforMicroscopicalAnalysisbyReflectedLightandDeterminationofMesophaseinaPitch1ThisstandardisissuedunderthefixeddesignationD4616;thenumberimmediatelyfollowingthedesignationindicatestheyearoforiginaladoptionor,inthecaseofrevision,theyearoflastrevision.Anumberinparenthesesindicatestheyearoflastreapproval.Asuperscriptepsilon(´)indicatesaneditorialchangesincethelastrevisionorreapproval.1.Scope1.1Thistestmethodcoverslaboratoryproceduresforthepreparationofgranularandmeltedsamplesformicroscopicanalysisusingreflectedlighttoidentifyandestimatetheamountandsizeofthemesophase.1.2Thevaluesstatedininch-poundunitsaretoberegardedasstandard.ThevaluesgiveninparenthesesaremathematicalconversionstoSIunitsthatareprovidedforinformationonlyandarenotconsideredstandard.1.3Thisstandarddoesnotpurporttoaddressallofthesafetyconcerns,ifany,associatedwithitsuse.Itistheresponsibilityoftheuserofthisstandardtoestablishappro-priatesafetyandhealthpracticesanddeterminetheapplica-bilityofregulatorylimitationspriortouse.2.ReferencedDocuments2.1ASTMStandards:2D329SpecificationforAcetoneD1160TestMethodforDistillationofPetroleumProductsatReducedPressureD2318TestMethodforQuinoline-Insoluble(QI)ContentofTarandPitchD3104TestMethodforSofteningPointofPitches(MettlerSofteningPointMethod)D4296PracticeforSamplingPitchE11SpecificationforWovenWireTestSieveClothandTestSievesE562TestMethodforDeterminingVolumeFractionbySystematicManualPointCount3.Terminology3.1DefinitionsofTermsSpecifictoThisStandard:3.1.1cenospheres—usuallyaminorcomponentofcoaltarpitch.Theyareformedbytherapidpyrolysisofunconfinedcoalparticlesthatarecarriedoverfromthecokeoventothetar.Microscopically,theyappearlikehollowspheresorseg-mentsthereof(seeFig.1),andaretypicallysizedfromabout10to500µm.Inpolarizedlight(crossedpolarizers),acenospheremaybeopticallyactive.Thesizeoftheanisotropicpatternormosaicdependsupontherankofthecoalcarbon-ized.Cenospheresareharderthanthecontinuousphaseandpolishinrelief(se...